What are you designed to eat?
Humans evolved over millions of years as hunter-gatherers, without eating large amounts of carbohydrates. We ate the food available to us in nature by hunting, fishing and gathering all the edible foods we could find. These foods did not include pure starch in the form of bread, pasta, rice or potatoes. We have only eaten these starchy foods for 5 – 10 000 years, since the development of agriculture. Just a limited adaptation of our genes takes place in such a relatively short time.
With the Industrial Revolution, 100 – 200 years ago, we got factories that could manufacture large amounts of pure sugar and white flour. Rapidly digested pure carbohydrates. We’ve hardly had time to genetically adapt to these processed foods. In the 80s, the fear of fat gripped the western world. Low-fat products popped up everywhere. But if you eat less fat you need to eat more carbohydrates to feel satiated. And it’s at this time in history that our disastrous epidemics of obesity and diabetes started. The most fat-phobic country in the world, the USA, was hit the hardest and is now the world’s most obese country. Today, it’s clear that the fear of real food with natural fat contents has been a big mistake. |
Why fat is the preferred fuel for human metabolism
|
The problem with starch and sugar.
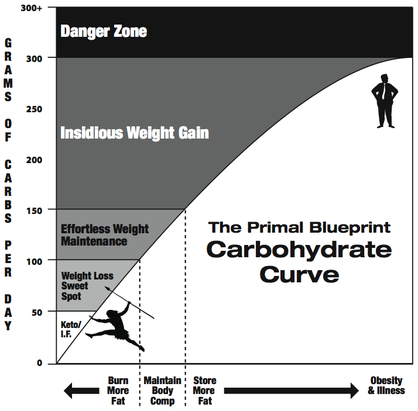
All digestible carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars in the intestines. The sugar is then absorbed into the blood, raising the blood glucose levels. This increases the production of the hormone insulin, our fat storing hormone.
Insulin is produced in the pancreas. In large amounts insulin prevents fat burning and stores surplus nutrients in the fat cells. After some time (a few hours or less) this may result in a shortage of nutrients in the blood, creating feelings of hunger and cravings for something sweet. Usually at that point people eat again. This starts the process again: A vicious cycle leading to weight gain.
On the other hand, a low intake of carbs gives you a lower, more stable blood glucose, and lower amounts of insulin. This increases the release of fat from your fat stores and increases the fat burning. This usually leads to fat loss, especially around the belly in abdominally obese individuals.
Insulin is produced in the pancreas. In large amounts insulin prevents fat burning and stores surplus nutrients in the fat cells. After some time (a few hours or less) this may result in a shortage of nutrients in the blood, creating feelings of hunger and cravings for something sweet. Usually at that point people eat again. This starts the process again: A vicious cycle leading to weight gain.
On the other hand, a low intake of carbs gives you a lower, more stable blood glucose, and lower amounts of insulin. This increases the release of fat from your fat stores and increases the fat burning. This usually leads to fat loss, especially around the belly in abdominally obese individuals.